US trade representative Jamieson Greer on Tuesday outlined the Trump administration’s rationale for imposing an 18% tariff on Indian goods, citing Washington’s large trade deficit with New Delhi.Greer said the US is working to formally finalise the trade agreement with India announced earlier this week and is in the process of putting the details on paper.
Why the US is imposing tariffs
Explaining the decision to retain a baseline 18% tariff, Greer said the move reflects the size and growth of India’s trade surplus with the US.“The reason we’re maintaining some level of tariff 18% is because we have this giant trade deficit with them,” he said, adding that India has agreed to reduce its tariffs on a range of US products.According to US Census Bureau data, India’s trade surplus with the US reached USD 53.5 billion during the first 11 months of 2025, compared to USD 45.8 billion for all of 2024.Under the agreement, the US will reduce tariffs on most Indian goods to 18% from 50%. “We’ll finish papering it, but we know the specifics, we know the details,” Greer said, adding that India is maintaining some protection around agricultural goods.
Zero tariffs on several US products
Greer said India has agreed to cut tariffs on American industrial goods to zero from 13.5% and reduce duties on a wide range of agricultural and manufactured products.“For a variety of things, you know, tree nuts, wine, spirits, fruits, vegetables, etc, they’re going down to zero,” he said.However, he did not mention rice, beef, soybeans, sugar or dairy products that India also excluded from its recent trade agreement with the European Union.
Agriculture, energy trade and Russian oil
Greer said the US would continue to push for greater access to protected areas of India’s agriculture sector and that the two sides had reached an understanding on technical barriers to trade.“We’ve reached an understanding and an agreement with the Indians as well on a variety of technical barriers to trade, areas where they have not accepted US standards. We know American goods are safe,” he said.He added that there would be “a process for recognising US standards,” though India would have to go through its own political processes before accepting them. Once implemented, he said, this would open a market of more than one billion people to more US goods.Greer also said the US administration has been closely tracking India’s energy trade patterns, particularly its imports of Russian crude oil.“Have been monitoring Indians winding down purchase of Russian oil,” he said, adding that there are “a lot of opportunities for India to diversify supply and buy more US product.”He said India did not import Russian oil prior to 2022 and 2023 and has been working since late last year to scale down such purchases.The remarks come after US President Donald Trump said on February 2 that Washington would cut reciprocal tariffs on Indian goods to 18% following a phone call with Prime Minister Narendra Modi, effectively sealing the deal.In a post on Truth Social, Trump said India had agreed to reduce tariffs and non-tariff barriers against the US to zero and committed to significantly higher purchases of American products.“They will likewise move forward to reduce their Tariffs and Non Tariff Barriers against the United States, to ZERO,” Trump said, adding that India had committed to buying over $500 billion worth of US energy, technology, agricultural and other products.
India confirms sensitive sectors protected
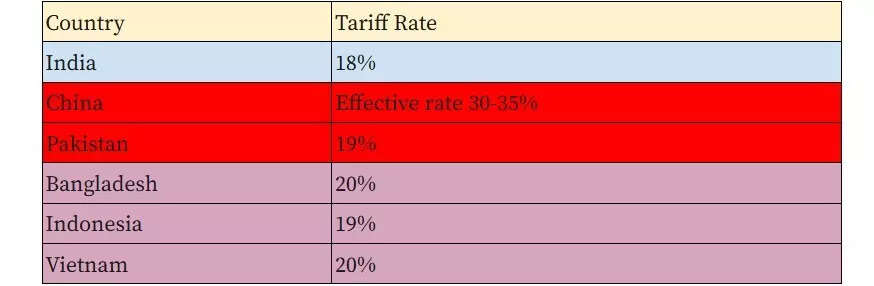
Commerce and industry minister Piyush Goyal said India has ensured that its sensitive agriculture and dairy sectors remain fully protected under the agreement.“The agreement will protect the sensitive sectors, the interests of our agriculture and our dairy sectors in full respect,” Goyal said at a press briefing.He said the deal would open opportunities for labour-intensive sectors such as textiles, apparel, home décor, leather and footwear, gems and jewellery, organic chemicals, rubber goods, machinery and aircraft, with US duties on these products coming down to 18% .Calling it a “very good” agreement, Goyal said Indian exporters are now better placed than competitors which continue to face higher tariffs in the US market.The reduction of US tariffs on Indian goods to 18% is expected to improve India’s competitiveness in the American market. Key competitor countries face higher tariffs, including Vietnam and Bangladesh at 20% , Malaysia at 19% , and Cambodia and Thailand at 19% each.
What the trade deal means and how India benefits
Under the proposed pact, India is expected to eliminate duties on some products immediately, phase out tariffs on others, and reduce import duties in select sectors. Certain items may also receive quota-based tariff concessions. Sensitive sectors such as agriculture and dairy, however, are completely excluded from the agreement, PTI reported.Greater clarity on tariff changes is expected through a US executive order and a joint India-US statement, both of which are awaited.The agreement is likely to benefit labour-intensive sectors that have been hit by steep US tariffs. These include garments, leather and non-leather footwear, gems and jewellery, plastics, chemicals, carpets and handicrafts. Exports from these sectors currently face tariffs of up to 50% , which will be reduced to 18% .Between 2021 and 2025, the United States remained India’s largest trading partner in goods. The US accounts for about 18% of India’s total exports, 6.22% of imports and 10.73% of overall bilateral trade.
Major traded products
In 2024, India’s key exports to the US included drug formulations and biologicals (USD 8.1 billion), telecom instruments (USD 6.5 billion), precious and semi-precious stones (USD 5.3 billion), petroleum products (USD 4.1 billion), gold and other precious metal jewellery (USD 3.2 billion), vehicle and auto components (USD 2.8 billion), ready-made cotton garments (USD 2.8 billion), and iron and steel products (USD 2.7 billion).Imports from the US included crude oil (USD 4.5 billion), petroleum products (USD 3.6 billion), coal and coke (USD 3.4 billion), cut and polished diamonds (USD 2.6 billion), electric machinery (USD 1.4 billion), aircraft and spacecraft parts (USD 1.3 billion), and gold (USD 1.3 billion).US services imports from India were estimated at USD 40.6 billion in calendar year 2024, led by computer and information services (USD 16.7 billion) and business management and consulting services (USD 7.5 billion).














